Neuroimaging Techniques
D. G. Norris
functional MRIlaminar fMRIpulse sequence developmentproton spectroscopy
We concentrate on the development and application of magnetic resonance imaging and spectroscopy (MRI/MRS) techniques for application in cognitive neuroscience and neurology. To this end my group currently has three research foci:
- Arterial Blood Contrast (ABC). By suppressing the grey matter signal using magnetisation transfer, the total signal from a voxel will increase when the blood volume increases, as happens during brain activation. In this way we hope to improve the spatial specificity of the fMRI experiment without compromising on the temporal resolution.
- Layer specific fMRI. Most fMRI experiments are performed at a spatial resolution of 2-3 mm, which is too coarse to resolve columnar and laminar structures. The ability to resolve activation at the level of the laminae potentially opens the possibility to interrogate feed-forward and feed-back relationships between different brain regions. We are now active in a number of projects studying language, cognitive control, and together with the group of Nikolai Axmacher (Bochum) the hippocampus.
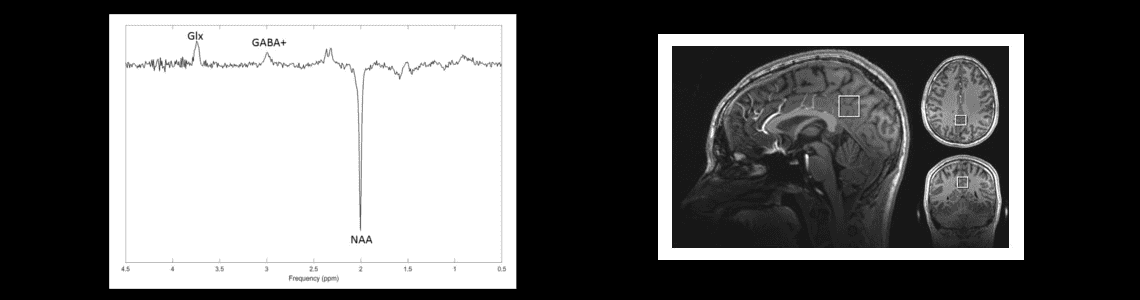
- Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) is the major inhibitory neurotransmitter in the brain. Glutamate is the major excitatory neurotransmitter. Both are detectable using proton spectroscopy (MRS). In a collaboration with MGH we are establishing protocols for interleaved measurement of 3D fMRI and MRS as these yield orthogonal information.
Current projects
- NWO: "Unravelling dopamine's role as gatekeeper of prefrontal cortex" 2022 - 2027
Selected Publications
- Hong D, SR Rankouhi, J Thielen, et al., A comparison of sLASER and MEGA-sLASER using simultaneous interleaved acquisition for measuring GABA in the human brain at 7T., PLoS One (2019)
- Lawrence SJ, DG Norris, FPd Lange, Dissociable laminar profiles of concurrent bottom-up and top-down modulation in the human visual cortex., Elife (2019)
- Lawrence SJD, Tv Mourik, P Kok, et al., Laminar Organization of Working Memory Signals in Human Visual Cortex., Curr Biol (2018)
- Markuerkiaga I, JP Marques, LJ Bains, et al., An in-vivo study of BOLD laminar responses as a function of echo time and static magnetic field strength., Sci Rep (2021)
- Markuerkiaga I, JP Marques, TE Gallagher, et al., Estimation of laminar BOLD activation profiles using deconvolution with a physiological point spread function., J Neurosci Methods (2021)
- Marques JP, DG Norris, How to choose the right MR sequence for your research question at 7T and above?, Neuroimage (2018)
- Meyer MC, R Scheeringa, AG Webb, et al., Adapted cabling of an EEG cap improves simultaneous measurement of EEG and fMRI at 7T., J Neurosci Methods (2020)
- Scheeringa R, M Bonnefond, Tv Mourik, et al., Relating neural oscillations to laminar fMRI connectivity in visual cortex., Cereb Cortex (2022)
- Scheeringa R, PJ Koopmans, Tv Mourik, et al., The relationship between oscillatory EEG activity and the laminar-specific BOLD signal., Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A (2016)
- Sharoh D, Tv Mourik, LJ Bains, et al., Laminar specific fMRI reveals directed interactions in distributed networks during language processing., Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A (2019)